The blockchain industry is still facing challenges with scalability and interoperability, which have persisted since Ethereum’s early days. Issues like high transaction fees, slow confirmation times, and isolated ecosystems are hindering the mainstream adoption of decentralized applications. Mango Network, a new Layer 1 blockchain developed by MangoNet Labs, claims to address these issues with a technical architecture that combines multiple virtual machines, cross-chain functionality, and high throughput capabilities.
Backed by $13.5 million in funding, Mango Network aims to process 297,450 transactions per second with 380-millisecond finality. It supports both Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) and Move Virtual Machine (MoveVM) in a unified ecosystem. The project’s Token Generation Event is scheduled for June 24, 2025, with $MGO tokens trading on Bitget, MEXC, and KuCoin at 09:00 AM UTC.
However, technical specifications alone may not guarantee success in the competitive Layer 1 landscape. This analysis delves into Mango Network’s architecture, tokenomics, and real-world potential to determine if it represents genuine innovation or another case of blockchain hype surpassing reality.
Technical Architecture: Multi-VM Innovation
The Move Programming Language Advantage
Mango Network implements “Mango Move,” an enhanced version of the Move programming language originally developed by Facebook for the Diem project. Move was designed specifically for digital assets, treating tokens and NFTs as primary elements in the programming model.
This resource-oriented approach offers several crucial advantages:
- Ownership Safety: Digital assets are represented as resources that cannot be copied or implicitly discarded, preventing double-spending attacks
- Static Typing: Every variable’s type is known at compile time, eliminating runtime bugs that plague other smart contract platforms
- Formal Verification: The Move Prover tool mathematically verifies smart contract behavior before deployment, enabling developers to specify contract logic in formal terms
- Modular Design: Smart contracts can be safely upgraded and composed without breaking existing functionality
Dual Virtual Machine Implementation
While Move enhances security for financial applications, Mango Network acknowledges that most DeFi protocols and tools are designed for the Ethereum Virtual Machine. To address this, Mango implements both EVM and MoveVM within the same blockchain.
This dual-VM approach allows EVM-based applications to run alongside Move-based contracts without interference. Each VM maintains its own state space while sharing the underlying blockchain infrastructure. Mango’s OP-Mango Layer 2 solution facilitates communication between EVM and MoveVM environments through standardized event capture and data serialization protocols.
The platform employs sophisticated resource allocation to prevent one VM from monopolizing network capacity. Transaction fees and execution limits are balanced across both environments to ensure fair access. Additionally, both virtual machines access a shared data availability layer to guarantee visibility of state changes across environments.
Modular Architecture
Unlike traditional blockchains that bundle multiple functions into single systems, Mango separates core functions: execution handles smart contract computation, consensus manages validator coordination via DPoS, settlement provides final transaction confirmation, and data availability stores transaction information across the network.
This separation enables each component to optimize independently while maintaining system integrity. The claimed 297,450 TPS throughput relies on this modular design, though actual performance may vary from theoretical maximums.
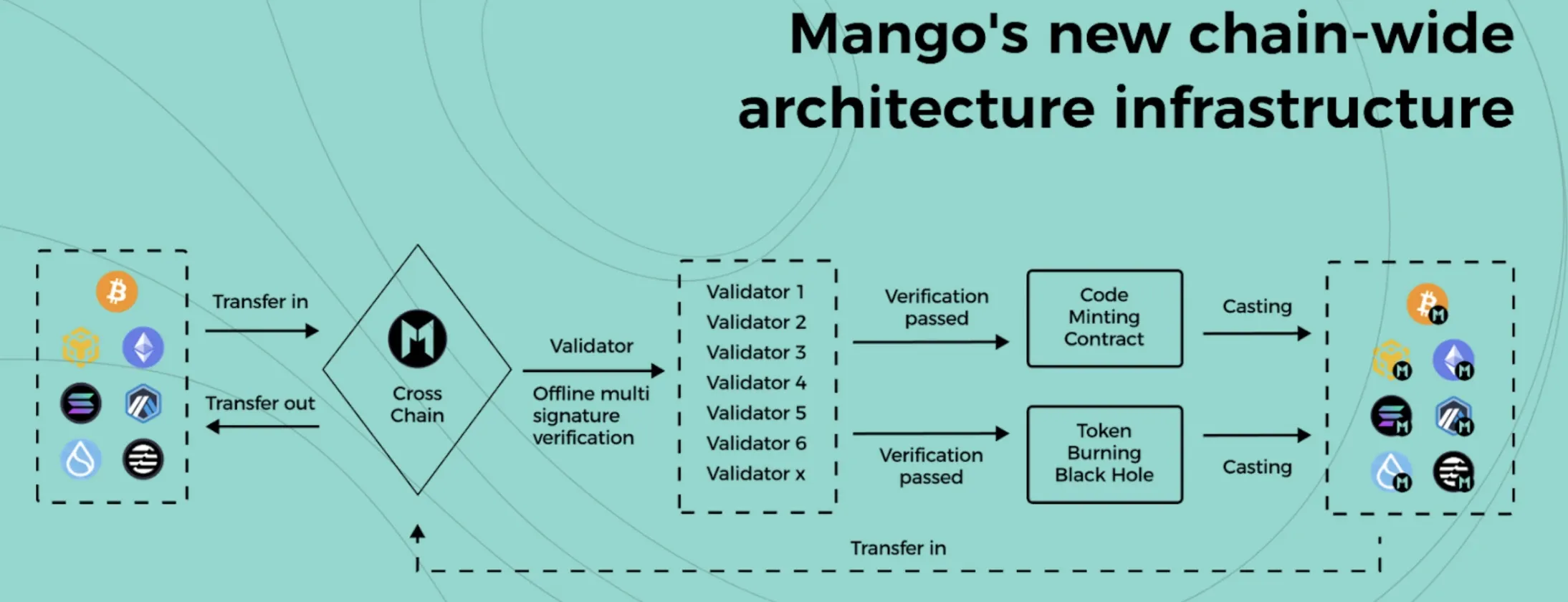
Mango’s chain infrastructure (official website)
Cross-Chain Infrastructure and Zero-Knowledge Integration
Cross-Chain Infrastructure and Privacy Features
OP-Mango facilitates cross-chain functionality by processing transactions off-chain in batches before submitting results to networks like Ethereum. $MGO tokens serve as gas for cross-chain operations, with fraud proof mechanisms in place to ensure security during asset transfers between blockchains.
Privacy and Storage Features
Mango Network incorporates ZK-SNARK and ZK-STARK technologies for privacy-preserving transactions and cross-chain transfers. Users can trade anonymously or move assets between chains without revealing transaction details. The platform also utilizes decentralized storage with economic incentives for storage providers earning $MGO tokens for data availability maintenance.
MgoDNS acts as the platform’s decentralized domain name system, bridging traditional internet and blockchain environments. It can resolve standard internet domain names while offering blockchain-specific features, such as a single domain name like “alice.mgo” resolving to wallet addresses on multiple blockchains. Smart contracts can automatically update domain resolutions based on programmed conditions.
Tokenomics Deep Dive
Distribution Strategy and Economic Model
The $MGO token has a total supply of 10 billion with immediate full unlock, deviating from typical token release schedules. The distribution allocates tokens across eight categories, with the Foundation and POS Stake Pool receiving the largest shares for development, operations, and network security.
Private investors, team, and early contributors also receive significant token allocations. Community airdrops make up 10% of the total supply, split between testnet and mainnet participants. Advisors receive the smallest allocation, reflecting their strategic role.
Token Utility and Value Drivers
The $MGO token serves various functions, including transaction fees, cross-chain operations, network security, governance rights, and ecosystem integration. However, the immediate token unlock strategy poses economic risks, potentially overwhelming demand and creating selling pressure.
Competitive Analysis and Market Positioning
Layer 1 Competition Landscape
Mango Network enters a competitive Layer 1 market dominated by established players like Ethereum and Solana. Move-based competitors Aptos and Sui also offer variations of the Move programming language. Mango’s high TPS claim and omni-chain vision compete with interoperability solutions like Cosmos and Polkadot.
Security Audit and Development Team
Professional Security Review
Mango Network underwent thorough security audits by MoveBit, covering core network and bridge operations. The audits identified and resolved issues, ensuring secure cross-chain functionality between Sui, Ethereum, and Mango chains.
Development Team and Leadership
The project’s leadership, including CEO Benjamin Kittle and CTO David Brouwer, emphasize transparency and open-source development. The team’s technical expertise and commitment to rigorous development practices bode well for Mango’s long-term success.
Ecosystem Applications and Adoption Strategy
DeFi and Cross-Chain Use Cases
Mango Network’s omni-chain approach promises unified liquidity pools across multiple blockchains, facilitating diverse asset interactions. The platform’s high throughput and low fees make it suitable for gaming applications and dynamic NFTs.
Enterprise Integration Potential
MgoDNS enables seamless integration of tokenized assets and blockchain tracking into traditional enterprise systems. However, enterprise adoption may be hampered by security and regulatory concerns.
Investment Analysis and Risk Assessment
Bull Case for Mango Network
Mango Network’s technical innovation and strong security foundation position it well for success in the blockchain infrastructure market. Encouraging signals like positive security audits and active development activities indicate potential for market adoption.
Positive Development Indicators
MoveBit’s security audits, substantial funding, and ongoing technical progress are positive indicators for Mango Network’s future success. The platform’s unique offerings in the Layer 1 market could attract quality developers and applications.
Risk Factors and Concerns
Execution risks, competitive challenges, and regulatory hurdles pose potential threats to Mango Network’s success. Immediate token unlock and market saturation could impact the platform’s growth and adoption rates.
Conclusion
Mango Network offers a technically advanced solution to blockchain infrastructure challenges. While facing risks and competition, the platform’s innovative approach and strong foundation position it as a contender in the Layer 1 market. The upcoming token launch and early performance metrics will be crucial in determining Mango Network’s long-term success.
For more information on Mango Network and airdrop eligibility, visitmangonet.io, or follow @MangoOS_Network for updates.

