As blockchain adoption continues to expand, so do the risks associated with it, such as frontrunning attacks, token scams, and cross-chain vulnerabilities. Blockchain security protocols play a crucial role in mitigating these risks by ensuring that every stage of a transaction — from initiation to confirmation — is safeguarded. Understanding the importance of end-to-end transaction security is essential for both users and developers to prevent losses and maintain secure network interactions. This article delves into the top protocols that are ensuring secure blockchain transactions in 2024.
Top 5 blockchain protocols
Here are some of the leading blockchain security protocols in 2024:
- Omnia Protocol – Provides frontrunning protection with private mempools
- LayerZero – Ensures secure cross-chain communication with private relayers
- Chainlink CCIP – Offers multi-layer validation for token transfers
- Wormhole – Utilizes guardian nodes for secure cross-chain transactions
- Cosmos Hub (IBC Protocol) – Facilitates secure asset transfers with Tendermint consensus
Now, let’s take a closer look at each of these blockchain security protocols.
1. Omnia Protocol: Best for preventing exploits
The Omnia Protocol is designed to provide secure and private access to blockchain networks, protecting users and developers from frontrunning, scam tokens, and malicious activities.
By ensuring the confidentiality of transaction data from start to finish, Omnia ensures end-to-end security and maintains the privacy of every blockchain operation.
Users: Omnia protocol
How it works?
Omnia acts as a secure tunnel for blockchain transactions, keeping data hidden from public view when users interact with a blockchain through its private RPC endpoints. Private mempools prevent bots from frontrunning trades or accessing sensitive information.
In addition, Omnia identifies and prevents scam tokens (honeypots) by analyzing smart contracts and transaction data in real-time.
Omnia is blockchain-agnostic and supports continuous transaction monitoring across multiple networks, ensuring comprehensive security coverage.
Pros
- Prevents frontrunning attacks: Private RPCs conceal transactions from bots.
- Blocks scam tokens: Honeypot detection prevents interactions with fraudulent tokens.
- Multi-chain support: Works seamlessly across various blockchains for enhanced flexibility.
Cons
- Technical setup: Users may require time to grasp private RPCs and honeypot protections.
- Node dependency: Continued node participation is necessary for uninterrupted access.
2. LayerZero: Best for secure cross-chain transactions
LayerZero ensures the safe and uninterrupted completion of transactions between different blockchains. Cross-chain transactions introduce new risks like frontrunning and incomplete transfers, which LayerZero addresses by securing every aspect of the transaction process.
Interface: Layer Zero
How it works?
LayerZero maintains speed and security by utilizing ultra-light nodes (ULNs), oracles, and relayers. It operates like a trusted courier network for sending packages, with relayers and validators confirming secure delivery from one blockchain to another.
ULNs validate transactions without requiring the entire blockchain’s data, ensuring agility and security.
Relayers transmit transaction data between blockchains while keeping it concealed from public view, preventing interception or manipulation.
Oracles independently verify transactions on both the source and destination chains, ensuring data integrity during cross-chain swaps.
LayerZero’s private relayers protect transaction data from manipulation or interception, while ULNs ensure secure validation for end-to-end transaction security.
Additionally, the modular design of each network component reduces the risk of system-wide vulnerabilities.
Pros
- Frontrunning mitigation: Private relayers keep transactions secure.
- Fast cross-chain execution: ULNs accelerate transactions without compromising security.
- Reliable verification: Oracles validate transactions accurately, safeguarding user assets.
Cons
- Complex setup: Initial understanding of relayers and oracles may be challenging for users.
- Dependency on validators: Efficient operation relies on validators functioning correctly.
3. Chainlink CCIP: Best for securing token transfers
Chainlink’s Cross-Chain Interoperability Protocol (CCIP) provides a secure method for transferring tokens between blockchains while preventing errors or manipulation. By validating transactions at multiple stages, CCIP ensures the security of transfers from start to finish, making it essential for safe cross-chain operations.
Chainlink protocol: Chainlink
How it works?
CCIP functions as a checkpoint system for blockchain transactions, with oracles and validators collaborating to confirm each step of the transfer process.
It operates similarly to sending a package through a series of post offices, where each stamp along the route ensures the package’s integrity before reaching its destination.
Chainlink CCIP employs multi-point validation, private communication channels, and flexible token handling to enhance security and prevent errors during transfers.
Pros
- Frontrunning protection: Keeps transactions private to prevent interference.
- Secure token transfers: Validates transactions at various points to prevent errors or loss.
- Cross-chain flexibility: Supports multiple networks for seamless asset movement.
Cons
- Learning curve: Users may require time to understand programmable transfers.
- Reliance on Oracles: Effective operation depends on validators and oracles functioning correctly.
4. Wormhole: Best with guardian verification
Wormhole facilitates secure asset and data transfers between multiple blockchains, reducing the risks associated with cross-chain transactions.
Through its guardian node system, Wormhole independently verifies each transaction, preventing unauthorized or tampered transfers and ensuring end-to-end transaction security.

Wormhole interface: Wormhole
How it works?
Wormhole acts as a bridge between blockchains, overseeing asset transfers with the assistance of guardian nodes. These nodes function as checkpoints on a highway, inspecting each transaction to ensure compliance with safety standards.
Before a transaction reaches the destination blockchain, guardian nodes validate it, rejecting any discrepancies to process only legitimate transfers. This approach maintains end-to-end transaction security, even when assets or data are transferred across different networks.
Wormhole’s decentralized bridge design and access to asset recovery tools set it apart from other blockchain security protocols.
Pros
- Guardian verification: Ensures secure transfers through independent validation.
- Decentralized security: Reduces dependence on a single validator, minimizing vulnerabilities.
- Recovery mechanisms: Provides tools for managing failed or stuck transactions.
Cons
- Bridge vulnerability risks: Like other cross-chain bridges, Wormhole is susceptible to evolving attack methods.
- Complex setup: Users may require time to comprehend the guardian node system.
Cosmos Hub: Best for secure asset transfers using the IBC protocol
The Cosmos Hub facilitates secure cross-chain transactions through its Inter-Blockchain Communication (IBC) Protocol, ensuring safe movement of assets and data between interconnected networks.
Cosmos Hub: Cosmos
How it works?
The IBC protocol functions as a secure delivery network for token transfers across blockchains. It mandates dual validation from both chains to complete a transfer. It operates like a two-way handshake: the sending chain locks the tokens, and the receiving chain issues an equivalent amount only after the first step is confirmed. Any issues during the process halt the transaction, safeguarding assets from loss.
IBC leverages Tendermint consensus to ensure trust and consistency among blockchains, guaranteeing accurate validation without delays or tampering.
Pros
- Prevents asset loss: Dual validation ensures assets remain secure during transfers.
- Fast and consistent: Tendermint consensus provides rapid validation without compromising security.
- Resilient to downtime: IBC can handle network disruptions and safeguard assets until recovery.
Cons
- Network coordination: Requires coordination across multiple blockchains, introducing complexity.
- Limited adoption: Integration of IBC into some networks is ongoing, limiting its current applications.
What is end-to-end transaction security?
End-to-end transaction security guarantees the protection of every transaction stage, from initiation to completion, against risks like manipulation, frontrunning, or incomplete execution.
This concept assures that no unauthorized entity can tamper with or alter a transaction, instilling confidence in users regarding their blockchain activities.
Without robust end-to-end security, blockchain transactions are vulnerable to frontrunning, phishing, or incomplete transfers.
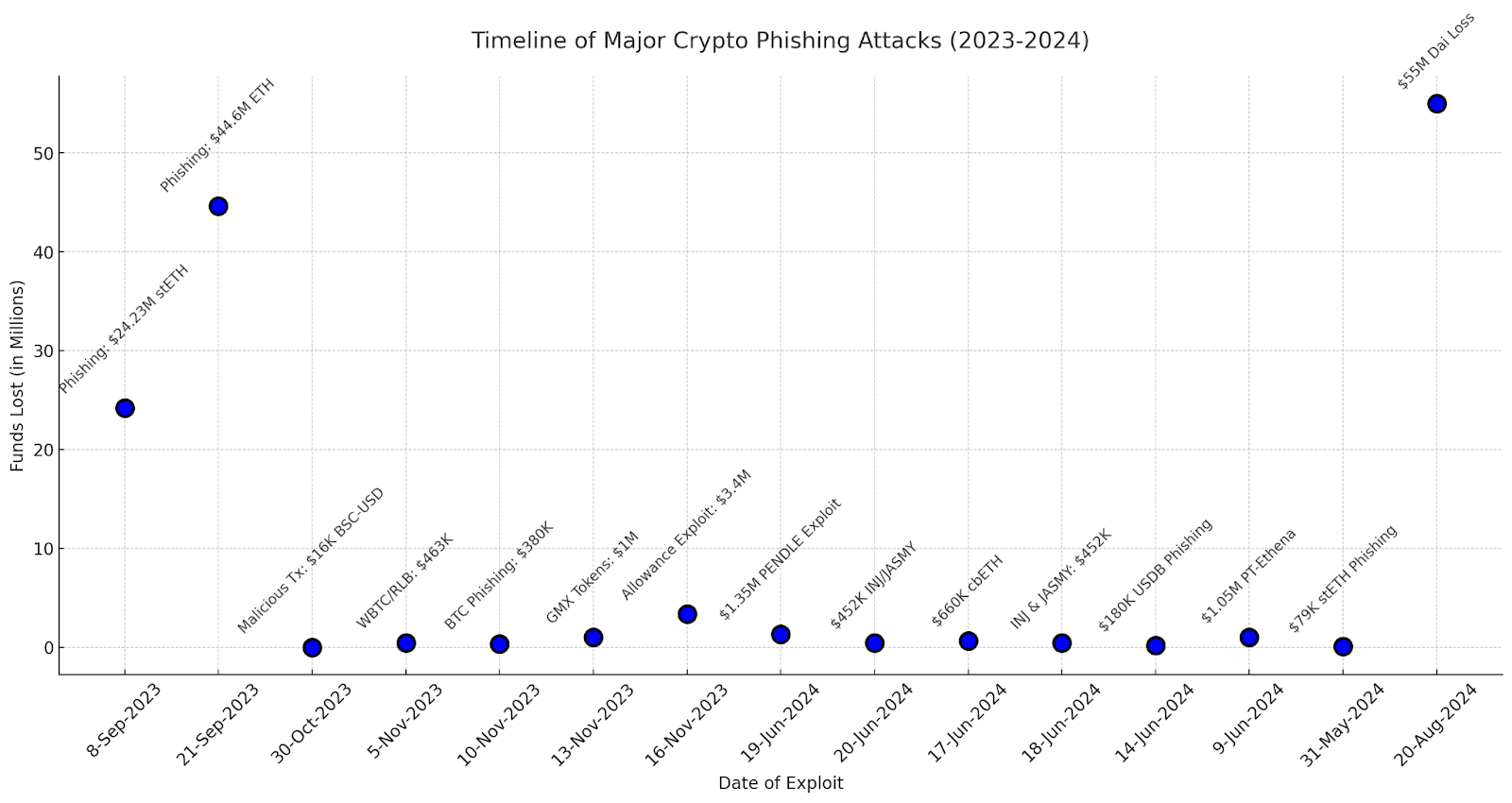
Timeline of major phishing events: BIC
Blockchain security protocols safeguard user funds, ensure trustworthy interactions with smart contracts, and prevent data leakage or manipulation during transactions.
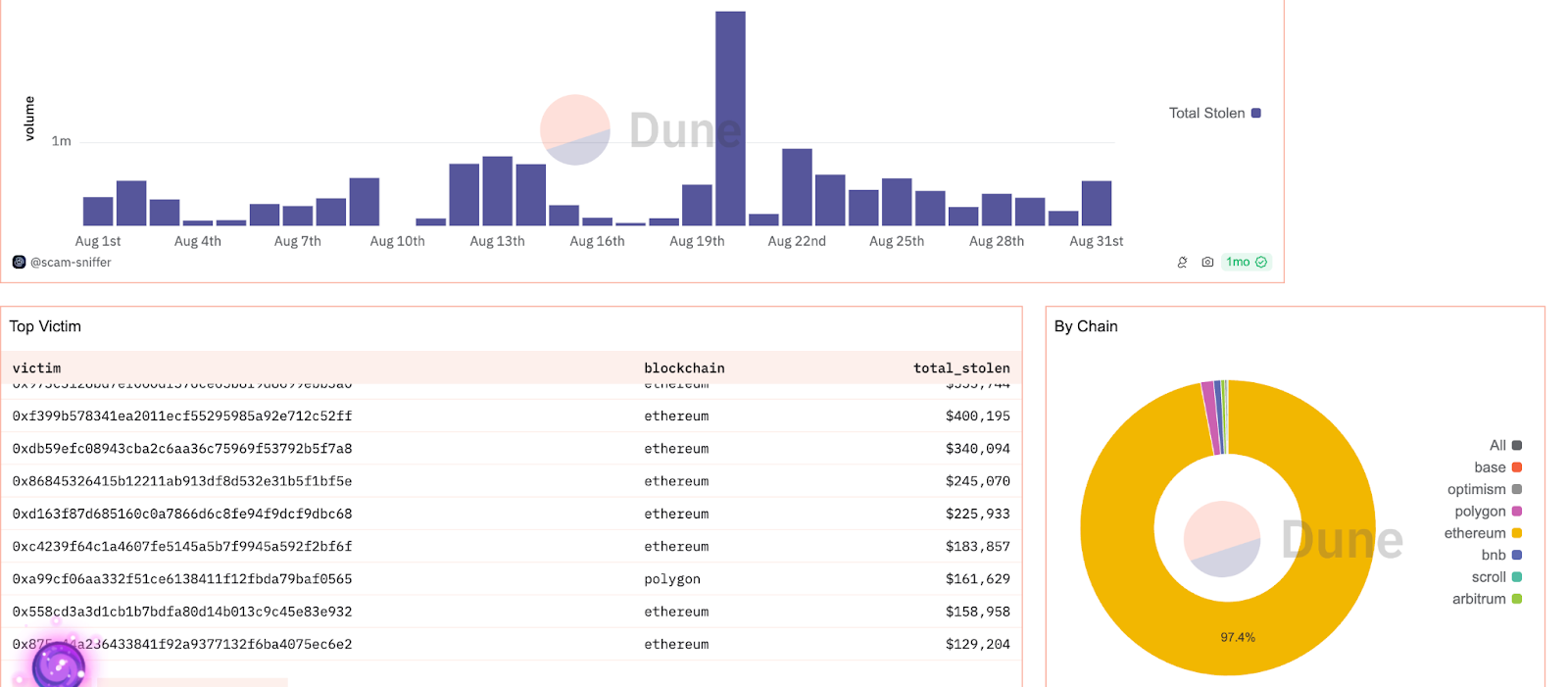
Recent phishing trends: Dune
Is it enough to secure transactions with blockchain security protocols?
While blockchain security protocols are crucial for ensuring safe transactions, they may not be sufficient on their own. Continuous upgrades are necessary to address evolving threats, alongside a multi-layered strategy involving user education, audits, and additional safeguards to enhance security and trust across decentralized networks.